|
CArl
Code Arlequin / C++ implementation
|
|
CArl
Code Arlequin / C++ implementation
|
Program responsible to calculate the coupled system solution of the FETI algorithm. More...
#include "CArl_FETI_solution.h"Go to the source code of this file.
Functions | |
| int | main (int argc, char **argv) |
Program responsible to calculate the coupled system solution of the FETI algorithm.
This program's input file description can be found at the documentation of the function carl::get_input_params(GetPot& field_parser, feti_set_sol_params& input_params).
It will use the following files from the input_params.scratch_folder_path folder:
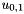 and
and 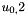 , from the system
, from the system 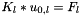 . Files:
. Files: ext_solver_u0_A_sys_sol_vec.petscvec ext_solver_u0_B_sys_sol_vec.petscvec
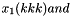 x_2(kkk), from the system
x_2(kkk), from the system 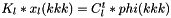 . Files:
. Files: ext_solver_A_sys_sol_vec.petscvec ext_solver_B_sys_sol_vec.petscvec
[RB] FETI_RB_correction.petscvec
The items marked with a [RB] are only needed if the rigid body modes projectors are used. In the last two cases, [nb. of vectors] is the number of rigid body mode vectors (given by input_params.nb_of_rb_vectors) and [iii] is an integer going from 0 to input_params.nb_of_rb_vectors - 1 (following C++ notation).
This program outputs the solution vectors inside the input_params.output_base folder. Files:
[input_params.output_base]_coupled_sol_A.petscvec [input_params.output_base]_coupled_sol_B.petscvec
Definition in file CArl_FETI_solution.cpp.
| int main | ( | int | argc, |
| char ** | argv | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 33 of file CArl_FETI_solution.cpp.